玩转 esbuild
前言
本篇来玩转 Vite 底层双引擎之一 -- esbuild,学习它的一些基本概念和功能使用,并实战开发一个完整的 esbuild 插件。
基本概念
esbuild 支持通过 cli 和 js api 调用,前者就不过多介绍了,无非就是通过各种 cli 参数控制打包行为,灵活性不是很高,简单的打包场景可以使用 cli 的方式,如果需要进行一些定制操作的话更多地会选择 js api。
而 js api 主要包括两个部分:
- Build API:针对整个项目而言,对项目进行打包
- Transform API:针对单个文件而言,对单个文件进行转译
基本使用
接下来会分别介绍一下 Build API 和 Transform API 的基本使用
Build API
接下来通过一些简单的 Demo 体验一下 Build API,这里主要介绍常用的三个:
- build
- buildSync
- serve
build & buildSync
const { build } = require('esbuild')
async function buildWithESBuild() {
const result = await build({
absWorkingDir: process.cwd(),
entryPoints: ['./src/index.jsx'],
outdir: './dist',
bundle: true,
format: 'esm',
external: [],
splitting: true,
sourcemap: true,
metafile: true,
minify: false,
write: true,
loader: {
'.png': 'base64',
},
})
console.log(result)
}
buildWithESBuild()
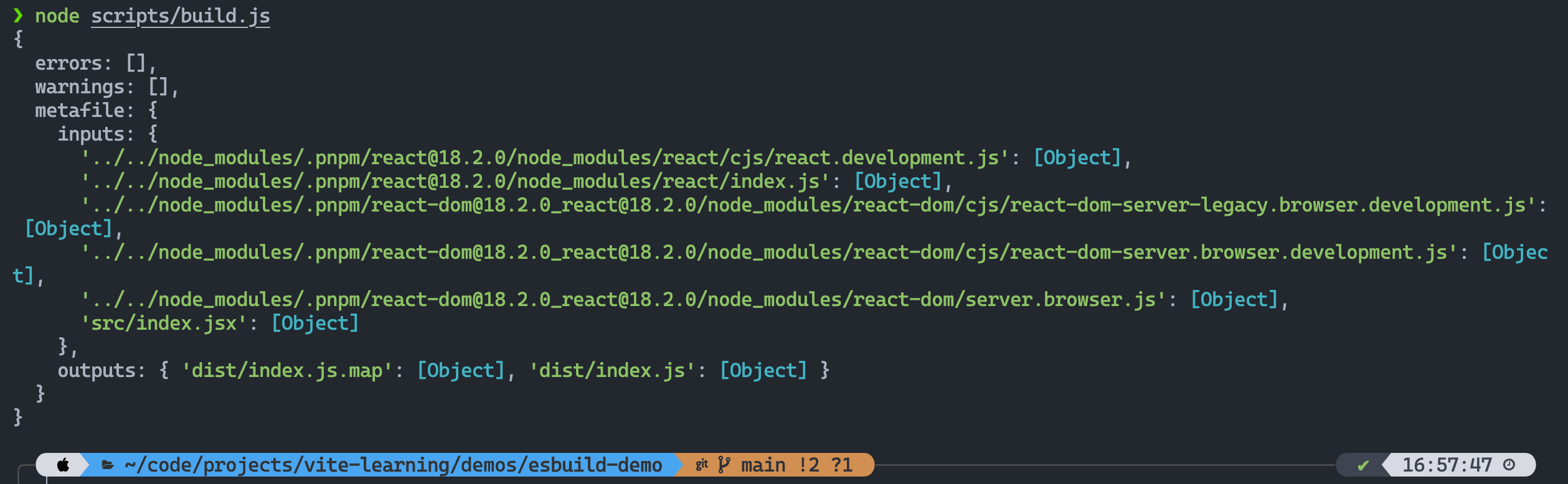
buildSync 和 build 使用上是类似的,从命名上能看出来一个是同步一个是异步,建议是使用 build 而不是 buildSync,因为如果使用 buildSync 的话,所使用的插件中 不能进行异步操作。
serve
serve 具有以下三个特点:
- 会启动一个 Golang 实现的服务器
- 类似于 webpack-dev-server,所有产物都不会写入磁盘,而是保存在内存中
- 每次请求到来时进行 rebuild,返回最新的产物
WARNING
rebuild 的时机是 请求到来,而不是 本地文件变更。
const { serve } = require('esbuild')
async function serveWithESBuild() {
const serveResult = await serve(
{
port: 8000,
servedir: './dist',
},
{
absWorkingDir: process.cwd(),
entryPoints: ['./src/index.jsx'],
outdir: './dist',
bundle: true,
format: 'esm',
external: [],
splitting: true,
sourcemap: true,
metafile: true,
minify: false,
write: true,
loader: {
'.png': 'base64',
},
},
)
console.log(`HTTP server starts at port: ${serveResult.port}`)
}
serveWithESBuild()
启动后就可以通过 http 访问构建后的产物了:
在新版 esbuild 中没有 serve 这个 API 了,变成用 context 替代,使用方式如下:
import * as esbuild from 'esbuild'
import http from 'node:http'
// Start esbuild's server on a random local port
let ctx = await esbuild.context({
// ... your build options go here ...
})
// The return value tells us where esbuild's local server is
let { host, port } = await ctx.serve({ servedir: '.' })
// Then start a proxy server on port 3000
http
.createServer((req, res) => {
const options = {
hostname: host,
port: port,
path: req.url,
method: req.method,
headers: req.headers,
}
// Forward each incoming request to esbuild
const proxyReq = http.request(options, (proxyRes) => {
// If esbuild returns "not found", send a custom 404 page
if (proxyRes.statusCode === 404) {
res.writeHead(404, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html' })
res.end('<h1>A custom 404 page</h1>')
return
}
// Otherwise, forward the response from esbuild to the client
res.writeHead(proxyRes.statusCode, proxyRes.headers)
proxyRes.pipe(res, { end: true })
})
// Forward the body of the request to esbuild
req.pipe(proxyReq, { end: true })
})
.listen(3000)
使用方式上的变化无需在意,只需要知道 esbuild 有这么个能力即可,以后再变化也可以直接跟着官方文档去查。
Transform API
与 Build API 类似,主要包括 transform 和 transformSync。
transform & transformSync
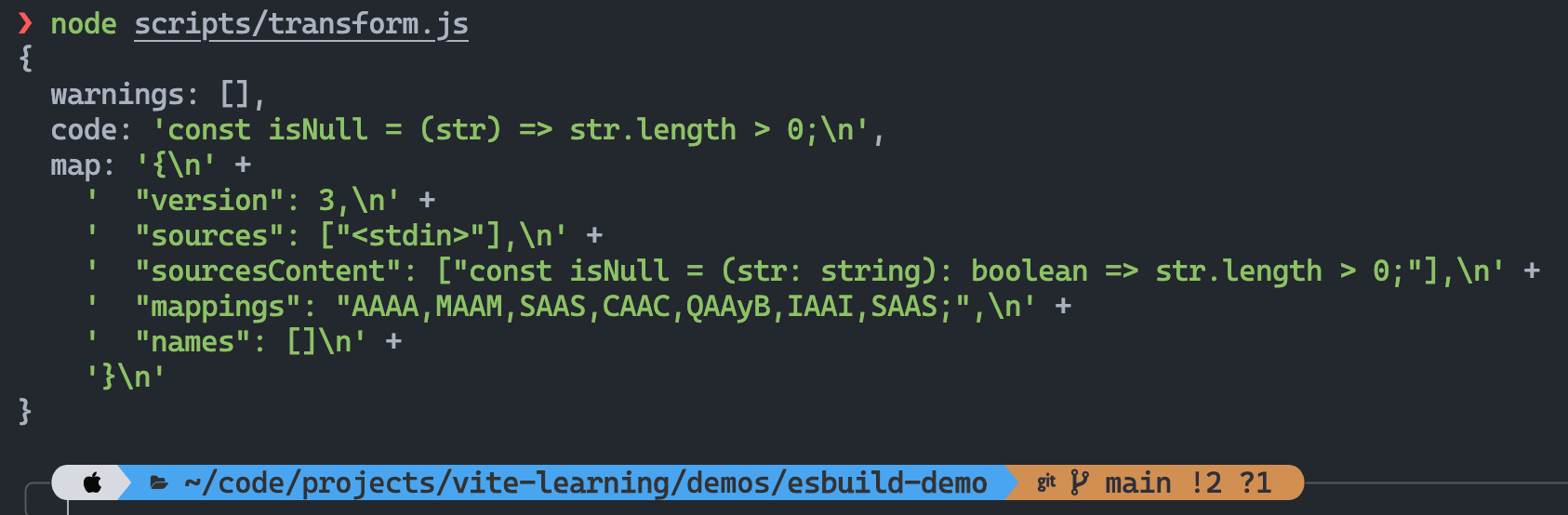
const { transform } = require('esbuild')
async function transformWithESBuild() {
const transformResult = await transform('const isNull = (str: string): boolean => str.length > 0;', {
sourcemap: true,
loader: 'tsx',
})
console.log(transformResult)
}
transformWithESBuild()
了解 esbuild 插件
插件开发的本质就是基于原有的体系结构基础上进行 扩展 和 自定义。
esbuild 的插件设计是一个对象,对象中有 name 和 setup 属性:
- name:插件名称
- setup:一个函数,入参是一个 build 对象,该对象上有一些钩子供我们自定义钩子函数的逻辑
体验一下吧!
下面是一个简单的示例:
build-with-demo-plugin.js
const { build } = require('esbuild')
const envPlugin = {
name: 'env',
setup(build) {
build.onResolve({ filter: /^env$/ }, (args) => ({
path: args.path,
namespace: 'env-ns',
}))
build.onLoad({ filter: /.*/, namespace: 'env-ns' }, () => ({
contents: JSON.stringify(process.env),
loader: 'json',
}))
},
}
function buildWithDemoPlugin() {
build({
entryPoints: ['./src/plugin-demo.js'],
bundle: true,
outfile: './dist/plugin-demo.js',
plugins: [envPlugin],
})
}
buildWithDemoPlugin()
entryPoints 的文件代码:
plugin-demo.js
// 应用了 env 插件后,构建时将会被替换成 process.env 对象
import { PATH } from 'env'
console.log(`PATH is ${PATH}`)
产物的代码如下:
;(() => {
// env-ns:env
var PATH = '/Users/root/.nvm/versions/node/v18.14.0/bin:/usr/local/bin'
// src/plugin-demo.js
console.log(`PATH is ${PATH}`)
})()
钩子简介
onResolve
负责控制路径解析行为:可以用于筛选要处理哪些路径。
上面的 Demo 中我们是这样使用该钩子的:
build.onResolve({ filter: /^env$/ }, (args) => ({
path: args.path,
namespace: 'env-ns',
}))
第一个参数是一个对象,用于决定插件要处理哪些文件,其包含两个属性:
- filter: 必填参数,是一个 RegExp,用于筛选要处理哪些文件
WARNING
这里的 RegExp 是用 Golang 里的 RegExp 语法,因此不能百分百兼容 JavaScript 的 RegExp,不支持:
- namespace: 可选参数,声明命名空间,用于后续在 onLoad 钩子中直接拿到筛选出的文件
onLoad
负责控制内容加载行为:可以以 onResolve 中解析出的 namespace 作为筛选项,获取要处理的模块路径,然后去决定加载这些路径时需要返回什么内容。
build.onLoad({ filter: /.*/, namespace: 'env-ns' }, (args) => {
console.log(`${'='.repeat(30)} onLoad ${'='.repeat(30)}`)
// 模块路径
console.log(args.path)
// namespace 标识
console.log(args.namespace)
// 后缀信息
console.log(args.suffix)
// 额外的插件数据
console.log(args.pluginData)
return {
// 模块具体内容
contents: JSON.stringify(process.env),
// 错误信息
errors: [],
// 指定 loader,如`js`、`ts`、`jsx`、`tsx`、`json`等等
loader: 'json',
// 额外的插件数据
pluginData: null,
// 插件名称
pluginName: 'xxx',
// 基准路径
resolveDir: './dir',
// 警告信息
warnings: [],
// 同上
watchDirs: [],
watchFiles: [],
}
})
对应的 stdout 输出如下:
============================== onResolve ==============================
env
/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/esbuild-demo/src/plugin-demo.js
file
/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/esbuild-demo/src
import-statement
undefined
============================== onLoad ==============================
env
env-ns
?xxx
undefined
onStart & onEnd
这两个钩子从命名上就能够知道它们的作用了,分别是在构建开始和构建结束时执行,就不过多介绍了。
插件开发实战
接下来通过两个需求来实战一下 esbuild 的插件开发:
- 通过 http 加载库
- 自动生成 html 引入产物
通过 http 加载库
我们一般加载模块时都是通过 import 导入相关库的包名,但如果想通过 http 去加载相关库的话是不支持的,比如从 cdn 加载 react 和 react-dom:
// react 和 react-dom 从 CDN 拉取
import { render } from 'https://cdn.skypack.dev/react-dom'
import React from 'https://cdn.skypack.dev/react'
let Greet = () => <h1>Hello, ESBuild!</h1>
render(<Greet />, document.getElementById('root'))
那么现在我们就自行开发一个插件来支持该功能!
首先需要在 onResolve 的时候决定我们需要处理 http 或 https 开头的路径
// 导入的模块是 http 链接的话需要进行处理
build.onResolve(
{
filter: /^https?:\/\//,
},
(args) => {
return {
path: args.path,
namespace: 'http-url',
}
},
)
我们来看看 cdn 返回的模块代码是怎样的:
/*
* Skypack CDN - react@17.0.1
*
* Learn more:
* 📙 Package Documentation: https://www.skypack.dev/view/react
* 📘 Skypack Documentation: https://www.skypack.dev/docs
*
* Pinned URL: (Optimized for Production)
* ▶️ Normal: https://cdn.skypack.dev/pin/react@v17.0.1-yH0aYV1FOvoIPeKBbHxg/mode=imports/optimized/react.js
* ⏩ Minified: https://cdn.skypack.dev/pin/react@v17.0.1-yH0aYV1FOvoIPeKBbHxg/mode=imports,min/optimized/react.js
*
*/
// Browser-Optimized Imports (Don't directly import the URLs below in your application!)
export * from '/-/react@v17.0.1-yH0aYV1FOvoIPeKBbHxg/dist=es2019,mode=imports/optimized/react.js'
export { default } from '/-/react@v17.0.1-yH0aYV1FOvoIPeKBbHxg/dist=es2019,mode=imports/optimized/react.js'
可以看到,会从 cdn 域名下的其他地方继续加载模块,因此我们也需要增加对这部模块的处理,因此需要再增加一个 onResolve:
// 拦截间接依赖的路径,并重写路径
// tip: 间接依赖同样会被自动带上 `http-url` 的 namespace
build.onResolve({ filter: /.*/, namespace: 'http-url' }, (args) => ({
// 重写路径
path: new URL(args.path, args.importer).toString(),
namespace: 'http-url',
}))
最后就是处理这些模块路径获取最终的内容,具体来说也就是下载对应的 http 资源并返回即可。
build.onLoad({ filter: /.*/, namespace: 'http-url' }, async (args) => {
const contents = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
async function fetch(url) {
console.log(`Downloading: ${url}`)
const httpClient = url.startsWith('https') ? https : http
const request = httpClient
.get(url, (response) => {
const statusCode = response.statusCode
if ([301, 302, 307].includes(statusCode)) {
fetch(new URL(response.headers.location, url).toString())
request.destroy()
} else if (statusCode === 200) {
const chunks = []
response.on('data', (chunk) => {
chunks.push(chunk)
})
response.on('end', () => {
resolve(Buffer.concat(chunks))
})
} else {
reject(new Error(`GET ${url} failed: status ${statusCode}`))
}
})
.on('error', reject)
}
fetch(args.path)
})
return {
contents,
}
})
最终完整代码如下:
import-http-plugin.js
module.exports = () => ({
name: 'esbuild:http',
setup(build) {
const http = require('http')
const https = require('https')
// 导入的模块是 http 链接的话需要进行处理
build.onResolve(
{
filter: /^https?:\/\//,
},
(args) => {
return {
path: args.path,
namespace: 'http-url',
}
},
)
// 拦截间接依赖的路径,并重写路径
// tip: 间接依赖同样会被自动带上 `http-url` 的 namespace
build.onResolve({ filter: /.*/, namespace: 'http-url' }, (args) => ({
// 重写路径
path: new URL(args.path, args.importer).toString(),
namespace: 'http-url',
}))
build.onLoad({ filter: /.*/, namespace: 'http-url' }, async (args) => {
const contents = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
async function fetch(url) {
console.log(`Downloading: ${url}`)
const httpClient = url.startsWith('https') ? https : http
const request = httpClient
.get(url, (response) => {
const statusCode = response.statusCode
if ([301, 302, 307].includes(statusCode)) {
fetch(new URL(response.headers.location, url).toString())
request.destroy()
} else if (statusCode === 200) {
const chunks = []
response.on('data', (chunk) => {
chunks.push(chunk)
})
response.on('end', () => {
resolve(Buffer.concat(chunks))
})
} else {
reject(new Error(`GET ${url} failed: status ${statusCode}`))
}
})
.on('error', reject)
}
fetch(args.path)
})
return {
contents,
}
})
},
})
接入一下该插件:
const { build } = require('esbuild')
const importHttpPlugin = require('./import-http-plugin')
async function buildWithImportHttpPlugin() {
await build({
entryPoints: ['./src/import-http-demo.jsx'],
outdir: './dist/import-http-demo',
format: 'esm',
bundle: true,
splitting: true,
sourcemap: true,
metafile: true,
plugins: [importHttpPlugin()],
})
console.log('Bundle finished!')
}
buildWithImportHttpPlugin()
运行后的 stdout:
Downloading: https://cdn.skypack.dev/react-dom
Downloading: https://cdn.skypack.dev/react
Downloading: https://cdn.skypack.dev/-/react@v17.0.1-yH0aYV1FOvoIPeKBbHxg/dist=es2019,mode=imports/optimized/react.js
Downloading: https://cdn.skypack.dev/-/react-dom@v17.0.1-oZ1BXZ5opQ1DbTh7nu9r/dist=es2019,mode=imports/optimized/react-dom.js
Downloading: https://cdn.skypack.dev/-/object-assign@v4.1.1-LbCnB3r2y2yFmhmiCfPn/dist=es2019,mode=imports/optimized/object-assign.js
Downloading: https://cdn.skypack.dev/-/scheduler@v0.20.2-PAU9F1YosUNPKr7V4s0j/dist=es2019,mode=imports/optimized/scheduler.js
Bundle finished!
这样一来就支持对 http 的模块进行 bundle 啦,是不是非常酷炫!
自动生成 html 引入产物
背景:
esbuild 打包出来的产物是 js 和 css,并不能直接运行,需要手动创建一个 html 文件去引入这些打包产物后才能使用,现在我们要开发的插件就是自动生成这个 html 文件。
实现思路是利用 onEnd 钩子能够从 metafile 中获取到所有产物的信息这一特点来遍历所有产物的构建信息,然后生成相应的 script 和 link 标签去加载它们。比较简单,就不过多赘述,直接看代码吧!
const fs = require('fs/promises')
const path = require('path')
module.exports = () => ({
name: 'esbuild:html-generator',
setup(build) {
build.onEnd(async (buildResult) => {
if (buildResult.errors.length) {
return
}
const { metafile } = buildResult
// 1. 拿到 metafile 后获取所有的 js 和 css 产物路径
const scripts = []
const links = []
if (metafile) {
const { outputs } = metafile
const assets = Object.keys(outputs)
assets.forEach((asset) => {
if (asset.endsWith('.js')) {
scripts.push(createScript(asset))
} else if (asset.endsWith('.css')) {
links.push(createLink(asset))
}
})
}
// 2. 拼接 HTML 内容
const templateContent = generateHTML(scripts, links)
// 3. HTML 写入磁盘
const templatePath = path.join(process.cwd(), 'index.html')
await fs.writeFile(templatePath, templateContent)
})
},
})
function createScript(src) {
return `<script type="module" src="${src}"></script>`
}
function createLink(src) {
return `<link rel="stylesheet" href="${src}"></link>`
}
function generateHTML(scripts, links) {
return `
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Esbuild App</title>
${links.join('\n')}
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
${scripts.join('\n')}
</body>
</html>
`.trim()
}



