玩转 rollup
前言
本篇来玩转 Vite 底层双引擎的另一位 -- rollup,同样也是学习它的基本使用和常用插件,并深入了解一下 rollup 的插件机制。
基本使用
主要包括 cli 使用方式和 js api 使用方式。
cli 使用方式
主要介绍一下 rollup 打包的常用配置,比较简单,这边直接贴代码看注释即可:
rollup.config.js
import { defineConfig } from 'rollup'
export default defineConfig(
// 可以传一个对象或一个数组,使用场景区别:
// - 对象:有一个或多个入口,但 output 配置是共用的
// - 数组:有多个入口,且 output 配置不同
[
{
input: ['src/index.js', 'src/utils.js'],
output: [
// {
// // 产物输出目录
// dir: 'dist',
// // 以下三个配置项都可以使用这些占位符:
// // 1. [name]: 去除文件后缀后的文件名
// // 2. [hash]: 根据文件名和文件内容生成的 hash 值
// // 3. [format]: 产物模块格式,如 es、cjs
// // 4. [extname]: 产物后缀名(带`.`)
// // 入口模块的输出文件名
// entryFileNames: `[name].js`,
// // 非入口模块(如动态 import)的输出文件名
// chunkFileNames: 'chunk-[hash].js',
// // 静态资源文件输出文件名
// assetFileNames: 'assets/[name]-[hash][extname]',
// // 产物输出格式,包括`amd`、`cjs`、`es`、`iife`、`umd`、`system`
// format: 'cjs',
// // 是否生成 sourcemap 文件
// sourcemap: true,
// // 如果是打包出 iife/umd 格式,需要对外暴露出一个全局变量,通过 name 配置变量名
// name: 'MyBundle',
// // 全局变量声明
// globals: {
// // 项目中可以直接用`$`代替`jquery`
// jquery: '$',
// },
// },
{
dir: 'dist/es',
format: 'esm',
},
{
dir: 'dist/cjs',
format: 'cjs',
},
],
// 对于某些第三方包,有时候我们不想让 Rollup 进行打包,也可以通过 external 进行外部化
// 在 SSR 构建或者使用 ESM CDN 的场景中,这个配置将非常有用
// external: ['react', 'react-dom'],
},
{
input: ['src/index.js'],
output: [
{
name: 'Foo',
dir: 'dist/umd',
format: 'umd',
},
{
name: 'Foo',
dir: 'dist/iife',
format: 'iife',
},
],
},
],
)
js api 使用方式
主要关注 rollup 提供的 rollup 和 watch 这两个 API:
- rollup: 用于 bundle
- watch: 用于监听文件变化时进行 bundle
接下来通过两个简单的 demo 体验一下:
rollup
import { rollup } from 'rollup'
// 常用 inputOptions 配置
const inputOptions = {
input: './src/index.js',
}
const outputOptionsList = [
// 常用 outputOptions 配置
{
dir: 'dist-with-build-script/es',
entryFileNames: `[name].[hash].js`,
chunkFileNames: 'chunk-[hash].js',
assetFileNames: 'assets/[name]-[hash][extname]',
format: 'es',
sourcemap: true,
globals: {
lodash: '_',
},
},
// 省略其它的输出配置
]
async function build() {
let bundle
let buildFailed = false
try {
// 1. 调用 rollup 生成 bundle 对象
bundle = await rollup(inputOptions)
for (const outputOptions of outputOptionsList) {
// 2. 拿到 bundle 对象,根据每一份输出配置,调用 generate 和 write 方法分别生成和写入产物
const { output } = await bundle.generate(outputOptions)
await bundle.write(outputOptions)
}
} catch (error) {
buildFailed = true
console.error(error)
}
if (bundle) {
// 最后调用 bundle.close 方法结束打包
await bundle.close()
}
process.exit(buildFailed ? 1 : 0)
}
build()
调用 rollup 后会生成一个 RollupBuild 对象,可以调用该对象的 generate 得到生成的 OutputChunk 去进行一些定制操作,但这些都只是在内存中进行,如果需要将产物真正写入到硬盘中,还需要调用该对象的 write 方法。
watch
直接看代码:
import { watch } from 'rollup'
const watcher = watch({
// 和 rollup 配置文件中的属性基本一致,只不过多了`watch`配置
input: './src/index.js',
output: [
{
dir: 'dist-with-watch-script/es',
format: 'esm',
},
{
dir: 'dist-with-watch-script/cjs',
format: 'cjs',
},
],
watch: {
exclude: ['node_modules/**'],
include: ['src/**'],
},
})
// 监听 watch 各种事件
watcher.on('restart', () => {
console.log('重新构建...')
})
watcher.on('change', (id) => {
console.log('发生变动的模块id: ', id)
})
watcher.on('event', (e) => {
if (e.code === 'BUNDLE_END') {
console.log('打包信息:', e)
}
})
启动后改动一下 src/index.js 后的 stdout 如下:
打包信息: {
code: 'BUNDLE_END',
duration: 40,
input: './src/index.js',
output: [
'/home/plasticine/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/dist-with-watch-script/es',
'/home/plasticine/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/dist-with-watch-script/cjs'
],
result: {
cache: { modules: [Array], plugins: [Object: null prototype] {} },
close: [AsyncFunction: close],
closed: false,
generate: [AsyncFunction: generate],
watchFiles: [Getter],
write: [AsyncFunction: write]
}
}
发生变动的模块id: /home/plasticine/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/index.js
重新构建...
打包信息: {
code: 'BUNDLE_END',
duration: 13,
input: './src/index.js',
output: [
'/home/plasticine/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/dist-with-watch-script/es',
'/home/plasticine/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/dist-with-watch-script/cjs'
],
result: {
cache: { modules: [Array], plugins: [Object: null prototype] {} },
close: [AsyncFunction: close],
closed: false,
generate: [AsyncFunction: generate],
watchFiles: [Getter],
write: [AsyncFunction: write]
}
}
可以让我们自定义监听文件变化时的行为。
常用插件
rollup 的插件系统生态十分丰富,能够让 rollup 具备一些额外的能力,比如:
- 支持 bundle 第三方库
- 支持处理 cjs 规范的入口模块
- 注入环境变量
- 配置路径别名
- 压缩产物代码
@rollup/plugin-node-resolve
该插件的官方文档介绍:
Locate modules using the Node resolution algorithm, for using third party modules in node_modules
rollup 官方文档的 troubleshooting 中有这样一句话:
Rollup will only resolve relative module IDs by default. This means that an import statement like this…
import moment from 'moment'
…won't result in moment being included in your bundle – instead, it will be an external dependency that is required at runtime. If that's what you want, you can suppress this warning with the external option, which makes your intentions explicit:
If you do want to include the module in your bundle, you need to tell Rollup how to find it. In most cases, this is a question of using @rollup/plugin-node-resolve.
即项目中依赖的第三方库默认是不会被 bundle 的,rollup 只会处理相对路径的模块,如果确实要 bundle 第三方库的话,需要使用 @rollup/plugin-node-resolve 插件让 rollup 支持解析 node 库的路径。
@rollup/plugin-commonjs
rollup 虽然能够打包出 cjs 格式的产物,但其接受的入口模块以及相关依赖都必须得是 esm 规范的模块才行。
虽然我们能保证开发自己的代码时使用 esm 规避这个问题,但是我们不能保证我们使用的第三方库提供的代码也是 esm 规范的,因此需要支持处理 cjs 规范的入口模块,这就是 @rollup/plugin-commonjs 所做的事情。
该插件的官方文档介绍也能很直观地体现它的作用:
Convert CommonJS modules to ES6, so they can be included in a Rollup bundle
接下来就安装一下 @rollup/plugin-node-resolve 和 @rollup/plugin-commonjs 来尝试把 lodash 这样一个只提供了 cjs 的第三方库打包进我们的 bundle 中吧!
pnpm i @rollup/plugin-node-resolve @rollup/plugin-commonjs
在 rollup.config.js 配置的 plugins 中注册一下这两个插件即可,这里也可以对比一下 esbuild 和 rollup 打包同样的代码所花费的时间:
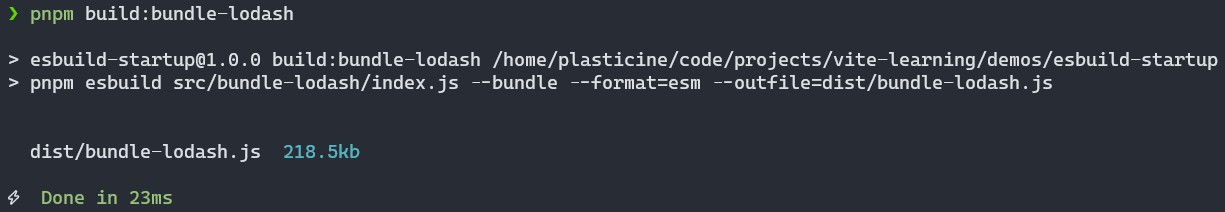
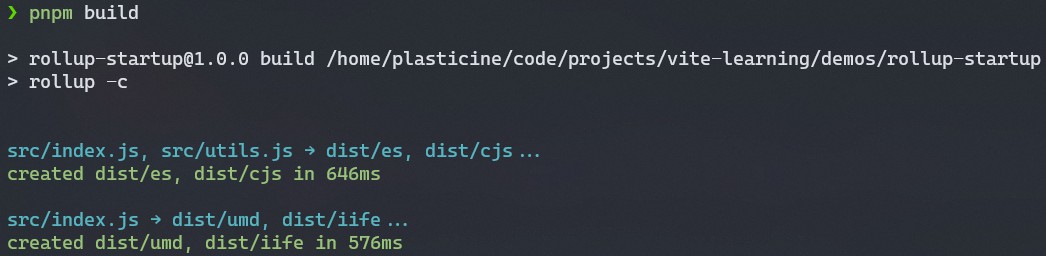
可以看到,esbuild 构建 esm 产物的耗时是 23ms,而 rollup 构建 esm 产物的耗时则是 646ms,esbuild 比 rollup 快了 28 倍!
其它插件
剩下的一些比较常用的 rollup 插件就简要介绍一下,不逐一演示了:
深入理解 rollup 插件机制
rollup 构建流程
当在 cli 中执行 rollup 后,其整个构建流程可以用简化后的代码表示:
// build 阶段
const bundle = await rollup.rollup(inputOptions)
// output 阶段
await Promise.all(outputOptions.map(bundle.write))
// end
await bundle.close()
也就是主要包括了:
- build 阶段:创建模块依赖图,初始化各个模块的 AST 以及模块之间的依赖关系
- output 阶段:生成输出产物的信息以及将产物写入硬盘
build 阶段
来看看 build 阶段生成的 RollupBuild 是个什么东西:
async function build() {
const rollupBuild = await rollup.rollup({
input: [resolve(__dirname, 'demo.js')],
})
console.log(inspect(rollupBuild, false, 100, true))
}
输出如下:
{
cache: {
modules: [
{
ast: { ... },
attributes: {},
code: "export const foo = 'foo'\n",
customTransformCache: false,
dependencies: [],
id: '/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/what-does-build-phase-do/module-foo.js',
meta: {},
moduleSideEffects: true,
originalCode: "export const foo = 'foo'\n",
originalSourcemap: null,
resolvedIds: [Object: null prototype] {},
sourcemapChain: [],
syntheticNamedExports: false,
transformDependencies: [],
transformFiles: undefined
},
{
ast: { ... },
attributes: {},
code: "import { foo } from './module-foo'\n\nconsole.log(foo)\n",
customTransformCache: false,
dependencies: [
'/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/what-does-build-phase-do/module-foo.js'
],
id: '/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/what-does-build-phase-do/demo.js',
meta: {},
moduleSideEffects: true,
originalCode: "import { foo } from './module-foo'\n\nconsole.log(foo)\n",
originalSourcemap: null,
resolvedIds: [Object: null prototype] {
'./module-foo': {
attributes: {},
external: false,
id: '/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/what-does-build-phase-do/module-foo.js',
meta: {},
moduleSideEffects: true,
resolvedBy: 'rollup',
syntheticNamedExports: false
}
},
sourcemapChain: [],
syntheticNamedExports: false,
transformDependencies: [],
transformFiles: undefined
}
],
plugins: [Object: null prototype] {}
},
close: [AsyncFunction: close],
closed: false,
generate: [AsyncFunction: generate],
watchFiles: [Getter],
write: [AsyncFunction: write]
}
可以看到,RollupBuild 是一个记录了各个模块的信息以及依赖关系,并没有生成产物也没有写入磁盘,如果需要完成这两步,则涉及到 output 阶段的 API。
output 阶段
output 阶段的 API 主要包括 RollupBuild 对象的 generate 和 write 方法。
generate 方法调用后会得到一个 RollupOutput 类型的对象,其记录了输出内容的相关信息,实际上 write 方法也能得到 RollupOutput,只是前者不会写入磁盘,后者会写入磁盘。
下面通过一个 demo 看看 RollupOutput 的结构。
generate
async function build() {
const rollupBuild = await rollup.rollup({
input: [resolve(__dirname, 'demo.js')],
})
const rollupOutput = await rollupBuild.generate({
format: 'esm',
})
console.log(inspect(rollupOutput, false, 100, true))
}
{
output: [
{
exports: [],
facadeModuleId: '/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/what-does-build-phase-do/demo.js',
isDynamicEntry: false,
isEntry: true,
isImplicitEntry: false,
moduleIds: [
'/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/what-does-build-phase-do/module-foo.js',
'/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/what-does-build-phase-do/demo.js'
],
name: 'demo',
type: 'chunk',
dynamicImports: [],
fileName: 'demo.js',
implicitlyLoadedBefore: [],
importedBindings: {},
imports: [],
modules: [Object: null prototype] {
'/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/what-does-build-phase-do/module-foo.js': {
code: [Getter],
originalLength: 25,
removedExports: [],
renderedExports: [ 'foo' ],
renderedLength: 18
},
'/Users/root/code/projects/vite-learning/demos/rollup-startup/src/what-does-build-phase-do/demo.js': {
code: [Getter],
originalLength: 53,
removedExports: [],
renderedExports: [],
renderedLength: 17
}
},
referencedFiles: [],
code: "const foo = 'foo';\n\nconsole.log(foo);\n",
map: null,
preliminaryFileName: 'demo.js',
sourcemapFileName: null
}
]
}
了解完 rollup 构建流程的两大阶段后就可以开始探索插件机制了,插件的各种钩子就是作用于这两大阶段的。
插件 hook 的类型
按构建阶段分类
按照 rollup 构建流程的两大阶段,插件 hook 的类型也可以对应分为两类:
- build hook: 作用于 build 阶段的 hook,对代码的操作粒度为 模块级别,即单文件级别
- output hook: 作用于 output 阶段的 hook,对代码的操作粒度为 chunk 级别(一个 chunk 是多个模块打包到一个文件的产物)
按执行方式分类
按执行方式大致可以分为以下几类:
- Async & Sync
- Parallel & Sequential: 相互之间无依赖关系的 hook 可以通过并发的方式执行,比如
buildStart;有依赖关系的则只能串行执行,比如 transform
- First: 有多个插件实现了某个 hook 时,会依次运行,直到其中一个 hook 返回非空值时停止,比如
resolveId
build 阶段 hooks 工作流
build 阶段的 hook 以及相应的工作流如下图所示:
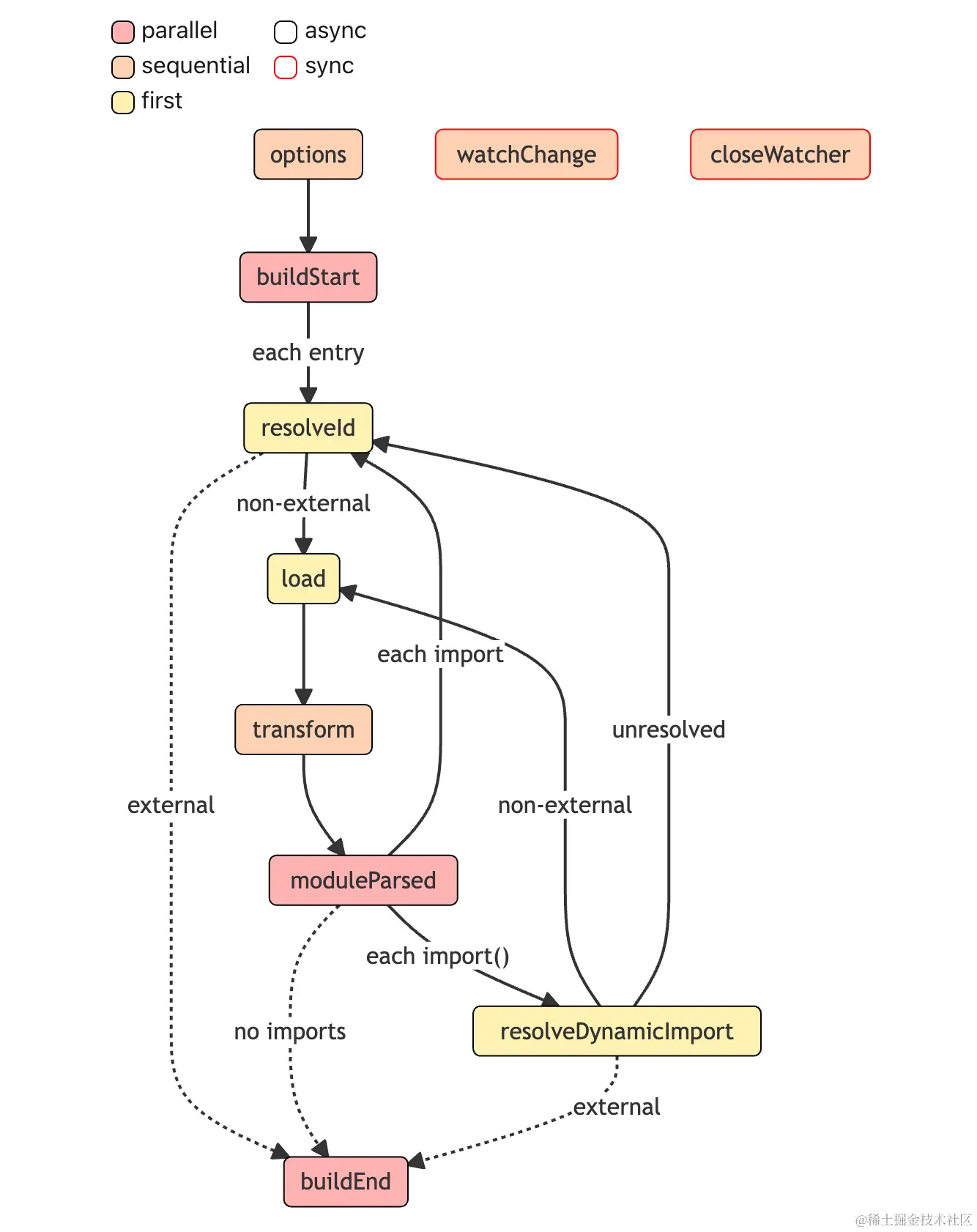
这里解释几个重点常用的 hook 的作用:
- resolveId: 解析文件路径,比如导入某个 npm 包,我们可以自定义解析到具体的某个 node_modules 里该包的路径
- load: 根据解析到的文件路径去加载对应的内容
- transform: 对 load 加载完成的模块内容进行转换,比如调用 babel 进行转译
- moduleParsed: 传入所有的 import 代码
- 静态 import,调用 resolveId
- 动态 import,调用 resolveDynamicImport,解析成功则继续走 load 的流程,否则降级到用 resolveId 兜底处理
TIP
对于配置了 external 的 id,不会执行 load 和 transform hooks。
output 阶段 hooks 工作流
output 阶段的 hook 以及相应的工作流如下图所示:

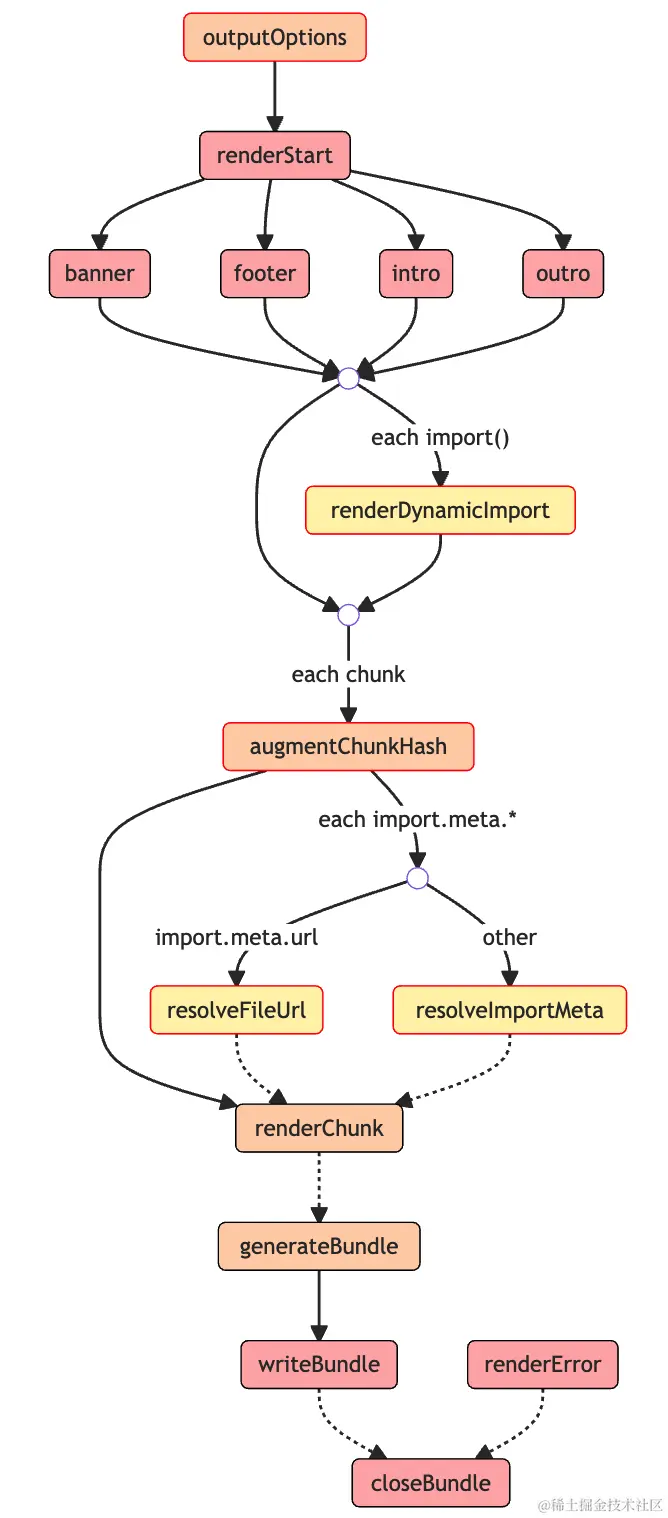
- outputOptions: 用于对 output 配置进行转换
- banner, footer, intro, outro: 往打包产物的相应位置插入自定义内容,比如协议声明、作者介绍、项目介绍等等
- renderChunk: 自定义操作每个生成的 chunk
- generateBundle: 入参是所有的 chunk 和 assets,可以自行决定是否删除掉某些 chunk 或 asset





